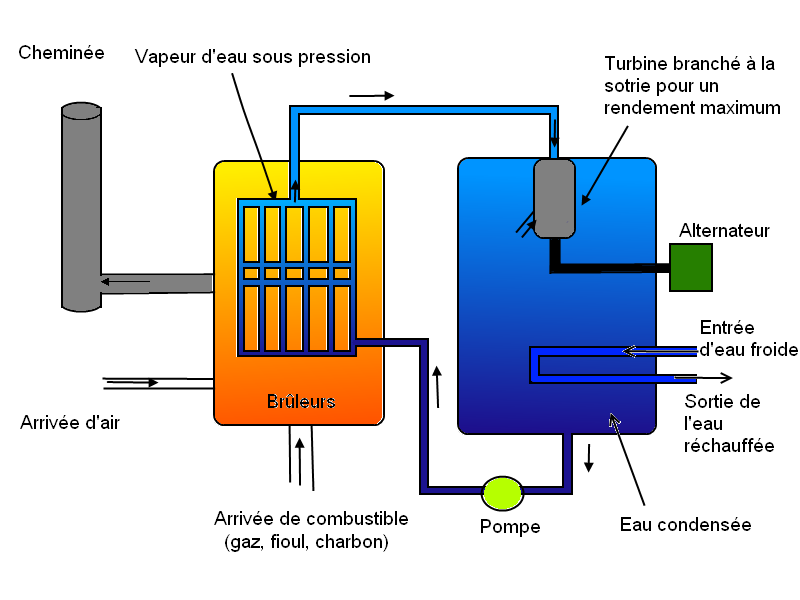
In this article, we take a look at advantages and disadvantages fossil-fired power plants. These structures are widely used to generate electricity, but they are not without their faults. We will review the strengths and weaknesses of these power plants to better understand their impact on the environment and society.
Visit France's only thermodynamic solar power plant
[arve url="https://www.youtube.com/embed/M7uYOFQ9xbo "/]
What are the advantages and disadvantages of fossil-fired power plants?
Fossil-fired power plants are facilities used to generate electricity by burning fossil fuels such as coal, oil and natural gas. They offer a number of important advantages and disadvantages.
Advantages :
- Power generation : Fossil-fired power plants have a high production capacity, making them a reliable energy source capable of meeting the growing demand for electricity.
- Flexibility : These plants can be rapidly started up or shut down, enabling them to adapt quickly to fluctuations in electricity demand.
- Low initial cost : Compared with other power generation technologies, fossil-fired power plants have a relatively low initial investment cost.
Disadvantages :
- CO2 emissions : The combustion of fossil fuels in these power plants results in significant emissions of carbon dioxide, a greenhouse gas that contributes to climate change.
- Air pollution : Fossil-fired power plants also emit other air pollutants such as nitrogen oxides, sulphur and fine particles, which have adverse effects on air quality and human health.
- Dependence on fossil fuels : These power plants depend on limited coal, oil and natural gas reserves, which raises issues of energy security and fuel price volatility.
Conclusion:
Fossil-fired power plants have advantages in terms of power generation capacity and flexibility, but they also have major drawbacks in terms of CO2 emissions and air pollution. They therefore need to be carefully assessed in the context of the global energy transition to cleaner, more sustainable sources of energy.
What are the disadvantages of a fossil-fired power plant?
The disadvantages of a fossil-fired power plant are as follows:
1. Greenhouse gas emissions : Fossil-fired power stations burn fossil fuels such as coal, oil or natural gas. This results in significant emissions of carbon dioxide (CO2) and other greenhouse gases responsible for global warming.
2. Air pollution : Fossil-fired power plants also emit atmospheric pollutants such as nitrogen oxides (NOx), sulfur dioxides (SO2) and fine particles. These pollutants have adverse effects on air quality and can cause health problems for neighboring populations.
3. Energy waste: Fossil-fired power plants have a relatively low efficiency, generally below 50%. This means that more than half the energy contained in the fuel is lost as waste heat. This is a considerable source of wasted energy.
4. Dependence on fossil fuels : Fossil-fired power plants depend on fossil fuels, which are non-renewable and finite resources. This dependence leads to geopolitical problems linked to fuel supply and contributes to unstable energy prices.
5. Risk of accidents : Fossil-fired power plants present a risk of accidents, particularly explosions and fires, which can cause major damage to the infrastructure and endanger the lives of people working in these facilities.
In conclusion, Although fossil-fired power plants can provide a steady, continuous source of energy, they have significant disadvantages in terms of environmental impact, public health, energy wastage and dependence on fossil fuels. It is therefore important to promote the development of cleaner, sustainable energy sources to reduce these disadvantages.
What are the advantages of a fossil-fired power plant?
A fossil-fired power plant offers several advantages:
1. High efficiency : Fossil-fired power plants are renowned for their high efficiency in converting the chemical energy of the fuel into electrical energy. This means they can produce a significant amount of electricity from a relatively small amount of fuel.
2. Flexibility of fuel use : Fossil-fired power plants can use a variety of fossil fuels such as coal, oil and natural gas. This enables them to adapt to fluctuations in the price and availability of different types of fuel.
3. Fast commissioning : Unlike nuclear power plants, which take years to build, fossil-fired power plants can be commissioned much more quickly. This makes them an attractive option for rapidly meeting growing electricity demand.
4. Operational flexibility : Fossil-fired power plants can easily adapt to variations in electricity demand. They can be rapidly started up or shut down according to the needs of the power grid.
5. Competitive production costs: Fossil-fired power plants generally have lower production costs than other energy sources, including renewables such as wind and solar. This makes them an affordable option for large-scale power generation.
6. Power grid stability : Fossil-fired power plants play an important role in ensuring the stability of the electricity grid, particularly at times of peak demand, when they can rapidly increase their electricity output to meet demand.
However, it should also be noted that fossil-fired power plants are often criticized for their high emissions of greenhouse gases, which have a negative impact on the environment and contribute to climate change. It is therefore essential to strike a balance between the use of fossil-fired power plants and the development of cleaner, sustainable energy sources.
What are the disadvantages of thermal energy?
Thermal energy has a number of disadvantages that are worth pointing out. Firstly, it contributes significantly to global warming and greenhouse gas emissions. Thermal power generation often requires the use of fossil fuels such as coal, oil or natural gas, which release carbon dioxide (CO2) when burned. These emissions contribute to climate change by increasing the greenhouse effect in the atmosphere.
What's more, the combustion of fossil fuels used in thermal power generation also generates harmful air pollutants such as nitrogen oxides and fine particles, which have a detrimental impact on air quality and human health. These pollutants can lead to respiratory problems, cardiovascular disease and even premature death.
What's more, thermal energy is heavily dependent on limited natural resources, notably oil and natural gas, whose reserves are gradually dwindling. This dependence can lead to energy price fluctuations and long-term security of supply problems.
Finally, the construction and operation of large-scale thermal power plants can lead to local environmental problems, such as the destruction of ecosystems, water and soil pollution, and risks associated with industrial accidents. For example, oil spills or gas leaks can cause considerable damage to the environment and surrounding communities.
It is therefore essential to take these drawbacks into account when discussing different energy sources, in order to find more sustainable and environmentally-friendly alternatives.
In conclusion, fossil-fired power plants have both advantages and disadvantages.
On the one handThey offer great operational flexibility, enabling a rapid response to electricity demand. What's more, these plants are relatively easy to build and require less installation time than other energy sources. They also contribute to grid stability by providing a constant source of generation.
On the other handFossil-fired power plants are extremely polluting, emitting large quantities of carbon dioxide and contributing to global warming. What's more, they depend on fossil fuels, a non-renewable resource whose prices can vary considerably. What's more, these power plants require large quantities of water to cool the systems, which can lead to water availability problems in regions already facing shortages.
All in allWhile fossil-fired power plants are a temporary solution for meeting electricity demand, they are not sustainable in the long term. It is crucial to invest more in renewable energies and clean technologies to reduce our carbon footprint and preserve our planet for future generations.