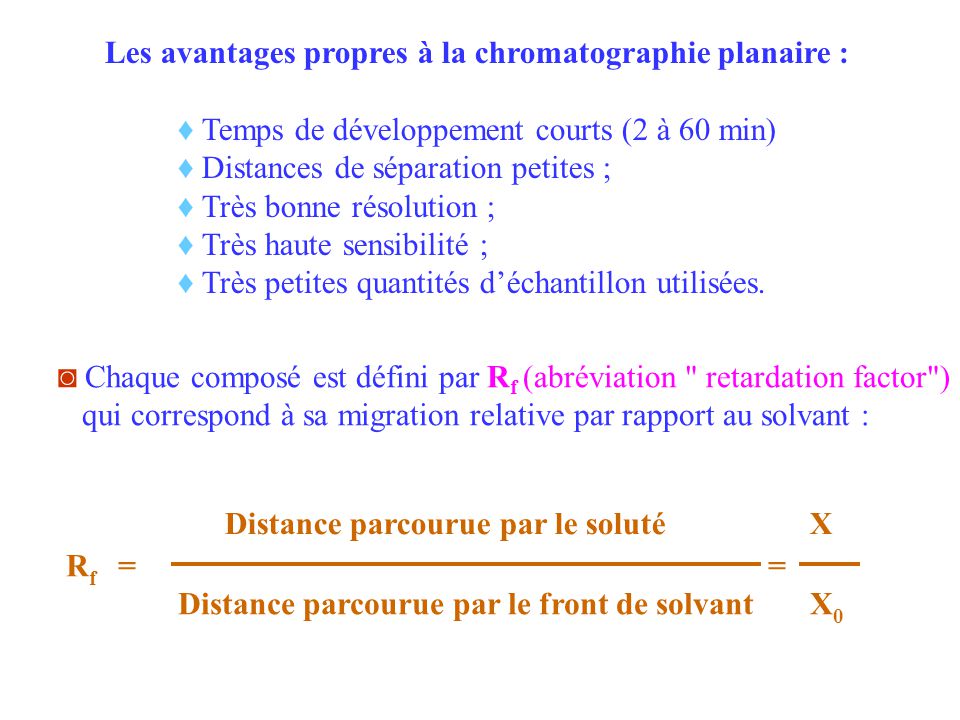
Visit thin-layer chromatography is an analytical technique widely used in chemistry to separate and identify the components of a mixture. The advantages of this method are many, including simplicity of use, low cost and speed of execution. However, not everything is perfect, as thin-layer chromatography also has certain drawbacks. disadvantagesThese include the need for great precision in sample preparation and a certain degree of subjectivity in interpreting results.
Thin layer chromatography: advantages and limitations
Principle of Thin Layer Chromatography (TLC) | Biochimie Facile
[arve url="https://www.youtube.com/embed/ySeWHW1d79k "/]
Gas chromatography GPC
[arve url="https://www.youtube.com/embed/yu1EUki7m5k "/]
What is the advantage of thin-layer chromatography?
Thin layer chromatography (TLC) is a very useful analytical technique in chemical and biochemical research. It separates the various components of a mixture according to their polarity. This technique is highly advantageous, as it offers great precision in the separation of compounds.
What's more, TLC is a fast, inexpensive method that uses very little solvent. It is therefore considered an environmentally-friendly alternative to other chromatography techniques, such as high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC).
Finally, TLC is highly versatile and can be used in many different applications, from food color analysis to drug purity testing. In short, thin-layer chromatography is a highly efficient analysis technique, offering many advantages for chemistry and biochemistry professionals.
What are the advantages and differences between column chromatography and thin-layer chromatography?
Column chromatography and thin-layer chromatography are techniques commonly used in chemistry to separate the various components of a mixture. However, they differ in their methodology and advantages.
Column chromatography involves the use of a column filled with packing material, such as silica gel or clay. The mixture is added to the top of the column, then a solvent is passed through the column, entraining the different components at different speeds depending on their affinity for the packing material. The components then exit the column separately and can be collected for later analysis.
The advantages of column chromatography include more precise separation of components, the ability to handle more complex mixtures, and the possibility of recovering pure products.
Thin layer chromatographyon the other hand, involves applying a sample to a support plate, such as silica or filter paper. This plate is then placed in an environment containing a solvent which moves along the plate, taking the various components with it. The components separate according to their relative affinity with the solvent and support, enabling them to be identified.
The advantages of thin-layer chromatography include its simplicity and speed, its low cost in terms of equipment and reagents, and the possibility of visually observing results.
In short, each of these methods has its advantages and disadvantages, depending on specific needs. It is important to choose the right method according to the mixture to be processed and the analysis objectives.
What is the choice of eluent for thin-layer chromatography?
The choice of eluent for thin-layer chromatography is as follows a crucial element in the separation and identification of compounds in a mixture. The choice of eluent depends on the properties of the compounds to be separated, such as their polarity and solubility.
There are different types of eluentThese include polar solvents (such as water and ethanol) and apolar solvents (such as hexane and toluene). The choice will therefore depend on the polarity of the compounds to be separated.
In general, a polar eluent will be used to separate polar compounds, while an apolar eluent will be used to separate apolar compounds. Mixtures of eluents can also be used to optimize separation.
In conclusion, the choice of eluent is a crucial element in thin layer chromatography. and must be carried out with care to achieve efficient separation and accurate identification of the compounds in the mixture being analyzed.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of thin-layer chromatography compared with other analytical methods?
Thin layer chromatography (TLC) is an analytical method widely used in chemistry and biology to separate and identify different compounds in a mixture. Its advantages are numerous: it's simple, fast, inexpensive and requires little specialized equipment. What's more, TLC can be adapted to a variety of samples, such as organic compounds, lipids or proteins. It is also useful for analyzing contaminants in foods and medicines.
However, CCM has a number of drawbacks. One of the main problems is its low resolution: it can only effectively separate compounds with significant differences in polarity. In addition, quantification of separated compounds can be more difficult than with other analytical methods, such as liquid chromatography (LC) or gas chromatography (GC). TLC can also be less accurate, as it uses lower quality standards in both stationary materials and samples, which can affect the reproducibility of results.
In short, although TLC is a useful analytical technique, it must be used with caution and in conjunction with other methods to ensure accurate and reliable results.
How can we optimize the results of thin-layer chromatography while minimizing its limitations?
Thin layer chromatography is a widely used analytical technique in chemistry and biochemistry. However, it does have certain limitations, such as low resolution and difficulty in identifying certain compounds. To optimize the results of this technique while minimizing its limitations, here are a few tips:
1. Use suitable solvents: Solvents used for elution must be chosen according to the nature of the compounds to be separated. It is important to select a solvent that allows good migration of the molecules without altering their structure.
2. Prepare the plate correctly: The quality of the thin film is crucial to obtaining satisfactory results. Careful plate preparation using appropriate solvents is recommended to avoid contamination and interference.
3. Develop the plate under optimum conditions: Plate development must be carried out under precise conditions, particularly with regard to temperature, humidity and the type of chamber used.
4. Use specific developers: Some developers may be more suitable than others, depending on the compounds you are looking for. So it's important to test several to find the one that's right for you.
By following these tips, you can optimize the results of thin-layer chromatography and minimize its limitations. Nevertheless, it should be remembered that this technique is only one tool among many, and that it is often necessary to combine several methods to obtain a complete and reliable analysis of samples.
Are there specific applications where thin-layer chromatography is particularly effective or ineffective?
There are really no specific applications where thin layer chromatography is particularly inefficient, as it can be used in a variety of fields to separate and identify compounds. However, some applications require high precision and very clear separation of components, and thin-layer chromatography may not be the most efficient method. For example, in the analysis of drugs or pharmaceuticals, where there are often several components present in small quantities, high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) is often preferred for its sensitivity and ability to separate closely related components. In the context of a news site, it would be interesting to mention recent developments in these fields, such as new HPLC methods or the discovery of new compounds by thin layer chromatography in the pharmaceutical and agricultural industries.
In conclusion, thin-layer chromatography is a useful and versatile technique for the separation and identification of chemical compounds. Its advantages include simplicity, speed and low cost, as well as the ability to separate complex mixtures. However, it also has drawbacks, such as its sensitivity to humidity, its lack of resolution for very similar compounds, and the need for specialized equipment. Nevertheless, despite its limitations, thin-layer chromatography remains an important tool in the field of chemical analysis.It is up to each researcher to assess whether this technique is suitable for their specific research objective.