Food irradiation: a controversial technology. Used to disinfect food, it offers advantages in terms of food safety, but also raises concerns about its effects on health and the environment. Find out more about advantages and disadvantages of this preservation technique in our article.
Food irradiation: benefits and risks
Food irradiation is a technique that involves subjecting food to ionizing radiation to eliminate micro-organisms and extend shelf life. This method has benefits such as reducing the risk of food poisoning and cutting food waste. On the other hand, it can also create risks to health if misused. High doses of radiation can alter the nutritional properties of foods and promote the appearance of toxic products. It is therefore essential inform consumers about the benefits and risks of this technique, so that they can make informed choices when buying irradiated foods.
Healthy or healing foods??? What we don't tell you!
[arve url="https://www.youtube.com/embed/nv2ojN5UER4″/]
Envoyé spécial. Qu'est-ce qu'on mange? - June 27, 2019 (France 2)
[arve url="https://www.youtube.com/embed/uCVly_8M5f8″/]
What is the reason for food irradiation?
Food irradiation is a treatment that uses ionizing radiation to eliminate or reduce pathogens in food. This technique has been used for many years to extend food shelf life and prevent food poisoning. It also reduces food waste by preserving food for longer.
However, the use of food irradiation is controversial as it can alter the taste, texture and nutritional quality of foods. Moreover, concerns remain about the safety of irradiated foods for human consumption.
In conclusion, Although food irradiation is an effective method of preserving food and preventing food-borne illness, it is important to continue studying the potential effects on consumer health, and to inform consumers about foods that have been subjected to this treatment.
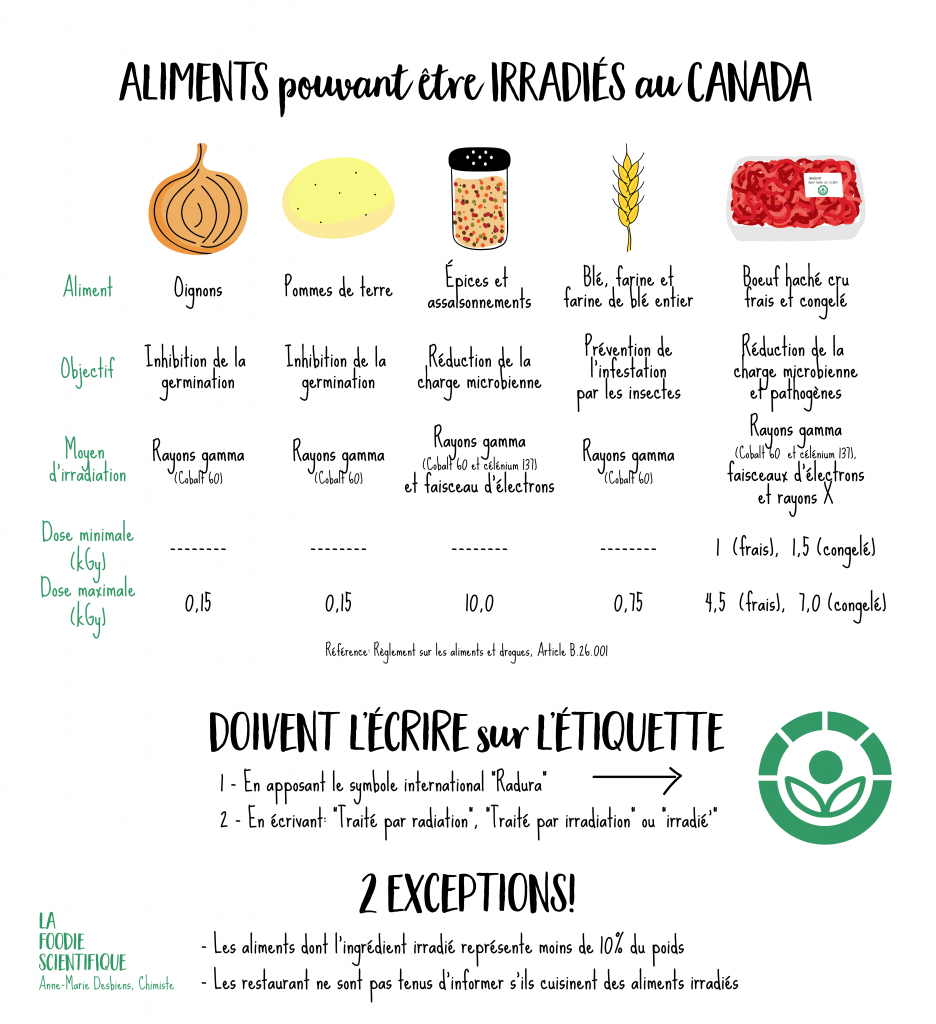
How can you tell if a food has been irradiated?
Irradiated foods must be labelled as such by law. Look for the label on the package. Irradiated foods are often treated to increase their shelf life. Foods that have been irradiated also often have a different texture and taste from those that have not. If you have any doubts about a food, you can also ask the grocery store or producer if it has been treated by irradiation.
What is the reason for irradiation?
Irradiation is carried out for several reasons in the context of the news. Firstly, it can be used to sterilize food to extend shelf life and make it safer to eat. Secondly, it can be used to decontaminate medical or pharmaceutical products, such as syringes or blood products. Finally, irradiation can be applied to combat the proliferation of bacteria and viruses in water or air. However, it is important to note that the use of irradiation also raises environmental and ethical concerns, which need to be carefully considered before applying this method.
What are ionized foods?
What are ionized foods? The food ionized are those that have been subjected to ionizing radiation treatment. This process involves exposing food to ionizing radiation, such as gamma rays or electrons, to destroy microorganisms and increase shelf life.
However, this treatment has given rise to controversy over its effects on health, as it can alter the molecular structure of foodstuffs, resulting in the formation of compounds that are potentially harmful to our bodies. As a result, some countries have banned the use of this technique on food intended for human consumption. In France, for example, only a few foodstuffs are authorized to be ionized, such as dried aromatic herbs, spices and certain meat preparations.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of food irradiation for food safety?
Food irradiation is a technique that involves exposing food to ionizing radiation such as gamma rays, X-rays or electrons to eliminate bacteria, viruses, parasites and molds. This technique can have both advantages and disadvantages for food safety.
The benefits:
– Reducing health risks: Food irradiation can eliminate up to 99.9% of harmful bacteria such as Salmonella, Escherichia coli and Listeria, as well as viruses such as norovirus. This improves food safety and reduces the risk of food-borne illness.
– Extended shelf life: Irradiation can inhibit the growth of microorganisms and delay the ripening process of fruit and vegetables, which can extend their shelf life. This can help reduce food waste and encourage the consumption of healthy foods out of season.
– Processing fragile food products: Irradiation can be used to treat fragile food products such as spices, herbs and seafood, without altering their taste, texture or appearance.
Disadvantages:
– Questions of perception: The technique of food irradiation is often controversial due to concerns about food safety and the preservation of nutrients and food quality. Some people may perceive irradiation as an "artificial" or "chemical" treatment that alters food.
– Cost: the cost of installing and maintaining irradiation equipment can be high, making this technique costly for food producers and processors.
– Compliance with regulations : The use of food irradiation must be regulated to guarantee consumer safety and avoid adverse effects on food quality. Standards and regulations vary from country to country, and can be difficult to implement.
In summary, food irradiation can be useful for improving food safety and extending shelf life, but it can also raise issues of perception, cost and regulation.
Is food irradiation safe for long-term human consumption?
Food irradiation is a preservation method that involves exposing food to ionizing radiation to eliminate bacteria, viruses and parasites that may be present in food. This method has been used since the 1960s, and is considered safe by many international organizations such as the World Health Organization (WHO) and the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA).
However, some consumer and expert groups question the long-term safety of this method. They point out that irradiation can alter the chemical structure of foods and create potentially toxic compounds. What's more, some experts are also concerned that irradiation can reduce the vitamin and essential nutrient content of foods.
Despite these concerns, scientific studies to date have concluded that irradiated foods are safe for human consumption in the short and long term, within the regulatory limits set by health authorities. In addition, irradiation is often used to prevent food-borne illness, which can be particularly beneficial for people with weakened immune systems, or for populations living in areas where the food supply is limited.
In the end, the decision to consume irradiated foods rests with the individual consumer. It is therefore important to be well informed about the advantages and disadvantages of this method of food preservation before making an informed decision.
How does food irradiation affect nutritional and organoleptic properties?
Food irradiation is the treatment of food with controlled exposure to ionizing radiation. While this can help reduce bacteria, parasites, molds and viruses in food to make it safer to eat, there are concerns about its effects on the nutritional and organoleptic properties of food.
Nutritional properties may be affected by food irradiation, as ionizing radiation can damage the vitamins and minerals present in foods. However, the effect depends on the irradiation dose and the sensitivity of the nutrients concerned. For example, vitamin C is sensitive to irradiation, while vitamin A is more resistant. Overall, nutritional losses due to irradiation are generally low and do not greatly affect the overall nutritional quality of foods.
Organoleptic propertiesThe sensory characteristics of foods, such as appearance, texture, odor and flavor, can be affected by food irradiation. Consumers may perceive an unpleasant taste or a strange odor in irradiated foods. However, this also depends on the irradiation dose and the type of food. Some foods, such as spices, herbs, fruits and vegetables, can be irradiated at higher doses without significantly affecting their organoleptic properties.
Ultimately, it is important to consider the advantages and disadvantages of food irradiation when it is used to improve food safety. Efforts must be made to minimize nutritional losses and undesirable organoleptic changes.
In conclusion, thefood irradiation offers significant advantages in terms of safeguarding quality and health safety. However, it is important to consider disadvantages associated with its use, particularly in terms of cost and environmental impact. In addition, some consumers may be reluctant to consume irradiated foods. Ultimately, food irradiation must be used judiciously, taking into account all aspects to ensure food safety while minimizing negative effects.