Visit de facto company is a little-known but interesting form of enterprise. It allows two or more people to work together without having to set up a formal company. However, this option is not without its drawbacks. In this article, we explore the advantages and disadvantages to help you decide if this is the right option for your business.
De facto partnerships: advantages and disadvantages
De facto companies are unregistered businesses formed by two or more people. One of the advantages of this type of structure is that it is simple and inexpensive to set up, as there is no need to register the business with any government body. In addition, profits are shared between the partners, and there is great flexibility in day-to-day operations. However, there are also disadvantages, such as the unlimited liability of the partners, who can be held responsible for the company's debts. What's more, it can be difficult for banks and other financial institutions to lend money to an unregistered business.
De facto partnerships are unregistered companies formed by two or more people. One of the advantages of this type of structure is that it is simple and inexpensive to set up.You don't have to register your company with any government agency. What's more, the benefits are shared between the partners, and there's a high degree of flexibility in day-to-day operations. However, there are also disadvantages, such as the unlimited liability of the partners, who can be held responsible for the company's debts. What's more, it can be difficult for banks and other financial institutions to lend money to an unregistered company.
SASU or EURL? Which legal status for sole traders? 👀 (SOLOPRENEUR/SELF-EMPLOYED)
[arve url="https://www.youtube.com/embed/ZNB9Uem9zA0″/]
SASU or EURL? How to choose your status in 2023?
[arve url="https://www.youtube.com/embed/np4iWZmbZh4″/]
What makes a de facto partnership special?
A de facto partnership is a company informal which operates without having been registered with the relevant authorities. It is also known as a "joint venture". Unlike conventional commercial companies, de facto partnerships do not have legal personality. distinct from that of its members. This means that the debts and commitments contracted by the de facto partnership directly and personally bind each partner.
This form of company is generally used for short-term projects, or when partners wish to join forces to carry out a common activity without having to create a specific legal entity. However, it is important to note that the de facto partnership can entail significant risks and legal consequences for its members. In the event of problems, they may have to pay for the company's debts, or face criminal sanctions.
It is therefore advisable to consult a lawyer or chartered accountant before setting up a de facto partnership. It is also advisable to draw up a written contract specifying the conditions of participation of the partners, as well as the sharing of profits and losses.
Who is responsible for a de facto company?
In the context of a news site, it is important to note that the de facto creation of a company is not recognized by lawIt is therefore essential to formalize the creation of the company by following the legal procedures in the relevant jurisdiction.
Once the company has been created in accordance with the law, the person in charge within the company depends on the type of corporate structure and the company's articles of association. In a public limited company (SA), for example, the Board of Directors is responsible for the general management of the company, and must be appointed by the General Meeting of Shareholders.
In a société à responsabilité limitée (SARL) or a entreprise unipersonnelle à responsabilité limitée (EURL), the manager is responsible for running the company. In all cases, the manager may be held liable for certain company activities, in particular in the event of mismanagement or non-compliance with legal and tax obligations.
It is therefore crucial for content creators to be aware of their responsibilities as founding members of a company, and to fully understand the legal implications of each corporate structure, so that they can choose the one best suited to their business and fulfill their legal obligations.
How do I register a sole proprietorship?
Registering a sole proprietorship is to set up a business with a single owner. Setting up a sole proprietorship in France can be done online via the official French administration portal.
To set up a sole proprietorship, follow these steps:
- Choose the company namewhich must not already be used by another company.
- Get a SIREN number and a SIRET number with INSEE.
- Determine the type of activity of the company.
- Establish a tax system for the company.
- If necessary, register with RCS (Trade and Companies Register).
Once all these steps have been completed, your sole proprietorship will be registered and you can start trading. Don't forget to take out professional indemnity insurance to protect your business and your customers.
What are the company's strengths and weaknesses?
The company's positive points are many. Firstly, technological advances have enabled information to be disseminated rapidly and efficiently throughout the world. (rapid, efficient dissemination of information). In addition, advances in medicine have led to a significant improvement in people's quality of life. (improved quality of life). Finally, the development of renewable energies has reduced the environmental impact of human activity. (reduced environmental impact).
However, there are also negative aspects to our society. Social and economic inequalities persist, despite efforts to reduce them (social and economic inequalities). Moreover, violence and crime are recurrent problems in certain regions of the world. (violence and crime). Finally, over-consumption and waste production continue to harm the environment and threaten our planet in the long term. (over-consumption and waste production). It is therefore important to take these problems into account and work together to solve them, in order to create a fairer, more sustainable society.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of a de facto partnership in terms of liability?
The advantages of a de facto partnership in terms of liability are as follows:
- Owners, also known as partners, are liable for the company's debts and obligations only up to the amount of their investment in the company. In this way, their liability is limited to their capital outlay, and they do not risk losing their personal assets if the company runs into financial difficulties.
- Associates are often involved in the management of the company, which means they can make better decisions because they have first-hand knowledge of how the organization works.
However, there are also disadvantages:
- The process of setting up a de facto company can be costly and complex, requiring major administrative steps such as registration with the Registre du Commerce et des Sociétés.
- As a legal entity, the de facto partnership may be held liable for its actions, and the partners may be considered jointly and severally liable if it fails to meet its obligations. In this case, they could be forced to pay sums in excess of their initial investment, putting their personal assets at risk.
- Finally, the separation between the company's affairs and the partners' personal affairs must be clearly established to avoid any conflict of interest or legal confusion, which can be difficult to manage for small businesses and sole traders.
How does a de facto partnership work and what are its tax advantages and disadvantages?
A de facto company is a business set up without the need to comply with the usual formalities of a company (such as registration in the commercial register). It is formed by a simple verbal or written agreement between two or more people, who have decided to work together to realize a common project.
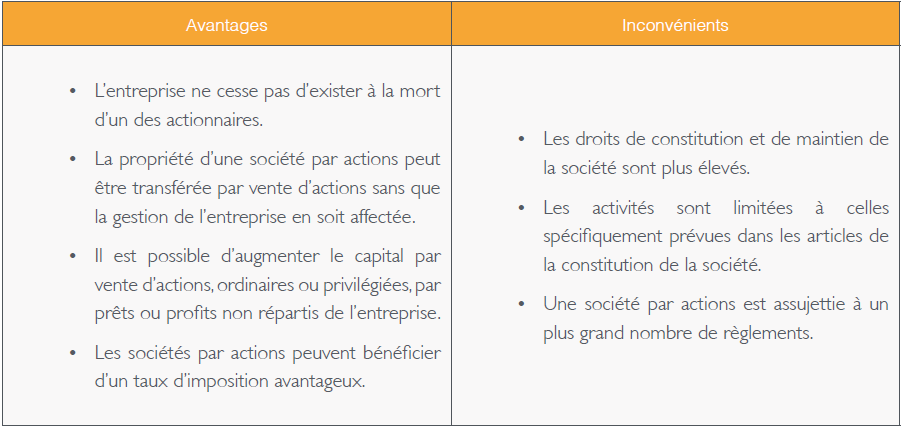
The advantages of a de facto partnership are many: it's quick and easy to set up, there are no set-up costs, and its members don't have to pay any specific social security contributions or taxes under this legal form. What's more, each member is individually liable for the company's actions and debts.
However, although the de facto company is simple and flexible, it also has tax disadvantages. Firstly, the profits made by the company are taxed on the income of the members, who must declare them individually and include them in their own tax returns. In addition, each member must keep separate accounts for the company's affairs, which can be tedious and complicated.
In short, a de facto partnership may be an attractive option for small projects or temporary activities, but it is not recommended for long-term ventures or those generating substantial profits. So it's important to think carefully about the most suitable legal form for your business before you launch.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of a de facto partnership compared with a sole proprietorship or a limited company?
The advantages of a de facto partnership
- Administrative simplicity: setting up a de facto partnership is relatively straightforward and inexpensive. There's no need to draw up articles of association or go through a notary to set it up.
- Independence: in a de facto partnership, partners have considerable freedom of decision and action. They can make decisions quickly and without specific administrative formalities.
- Tax transparency: each partner declares his or her share of profits in his or her personal tax return, which facilitates company taxation.
The disadvantages of a de facto partnership
- Unlimited liability: in a de facto partnership, each partner has unlimited liability for the company's debts. This means that creditors can turn against the personal assets of each partner in the event of financial difficulties for the company.
- Difficulty in obtaining financing: banks are often reluctant to lend money to a de facto company, as there is no share capital and no particular guarantee.
- Low durability: a de facto partnership is often less stable than a sole proprietorship or a limited company. Indeed, if one of the partners decides to leave the company, it may be dissolved if the other partners do not wish to continue the business.
Comparison with a sole proprietorship or a limited company
- A sole proprietorship is often simpler to set up and manage than a de facto company. However, the manager has unlimited liability for the company's debts, which can be a major risk.
- A limited liability company (SA, SAS, SARL) can offer better legal protection for partners and easier access to financing. On the other hand, setting up and managing such a company is often more complex and costly than in the case of a de facto partnership.
In conclusion, the de facto company has both advantages and disadvantages. On the one hand, it offers a great deal of freedom in terms of how the company is organized and run, as well as flexibility in terms of tax and social security. On the other hand, it exposes associates to unlimited personal risk with regard to the company's debts, and can give rise to difficulties in terms of financing or succession. The decision to set up a de facto partnership must therefore be carefully considered and adapted to each individual case. It is advisable to be accompanied by a legal professional to assess the various options and make an informed decision.