Hybrid plants, the result of crossing different varieties, offer interesting advantages for gardeners and growers. They often combine characteristics such as disease resistance, higher productivity or more abundant flowering. However, certain disadvantages such as loss of biodiversity or the need for artificial reproduction must also be taken into account. In this article, we take a closer look at the advantages and disadvantages of hybrid plants.
LOA & LLD: Scams. Why are they scams?
[arve url="https://www.youtube.com/embed/0t9C9r6JZ3c "/]
What are the advantages of hybridization?
Hybridization offers many advantages in the context of a news site.
First and foremost, hybridization reaches a wider audienceby combining different content formats. For example, by offering a mix of written articles, videos and podcasts, we can attract different types of readers and adapt to their information consumption preferences.
Next, hybridization boosts user engagement. By offering a variety of formats, readers are given the opportunity to choose how they prefer to be informed. Some may prefer to read articles, while others may be more interested in videos or podcasts. Adapting content to different preferences increases the time spent on the site, and therefore user engagement.
What's more, hybridization diversifies information sources. By integrating content from different media (written, audiovisual, etc.), we can offer a more complete and balanced perspective on the subjects covered. This strengthens the site's credibility and gives users access to more diverse and rich information.
Finally, hybridization offers greater flexibility in information distribution. By using different formats, you can adapt the way you tell a story or present a news item, depending on its nature and importance. For example, for urgent news, a video or push alert may be more appropriate, while for in-depth analysis, a written article may be more suitable.
In short, hybridization offers a number of advantages in the context of a news site, making it possible to reach a wider audience, encourage user engagement, diversify information sources and offer greater flexibility in the dissemination of information.
Why can't F1 seeds be reproduced?
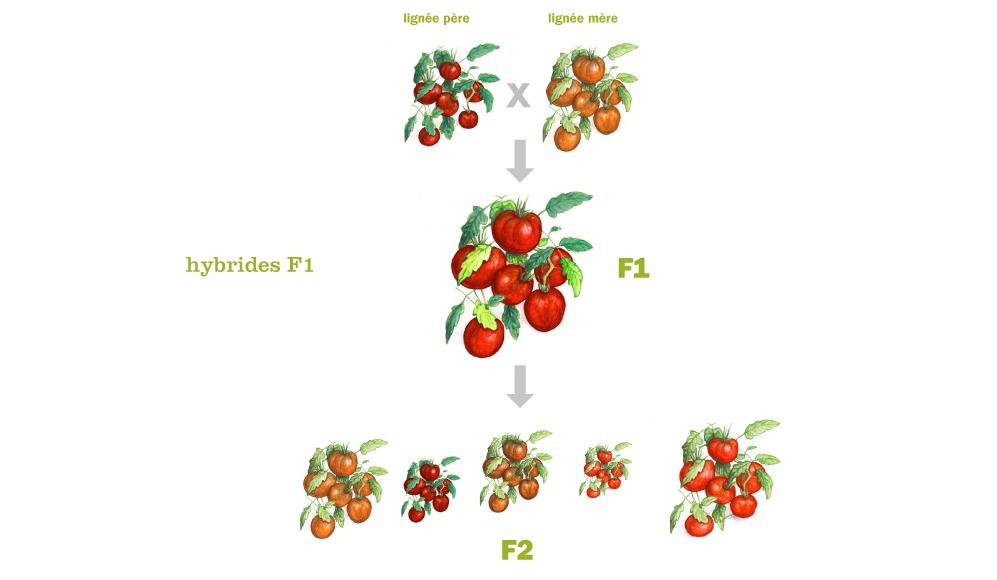
F1 seeds are not reproducible because they are the result of crossing two different parents, known as pure lines. These parents are carefully selected for their specific characteristics, such as disease resistance, productivity or taste. The result of this crossing is a hybrid plant, known as an "F1".
However, when F1 seeds are harvested and resownHowever, they will not necessarily produce plants that exactly resemble the original plant. This is due to a phenomenon known as "genetic segregation", where the characteristics of the parents mix randomly during reproduction.
As a result, each subsequent generation of F1 seeds will produce variations of plants with different characteristics. This makes F1 seeds unreliable for reproduction, as they do not guarantee the stability of the desired characteristics.
For this reason, farmers and gardeners have to buy new F1 seeds every year if they want to grow the same hybrid plants. This helps maintain the uniform, consistent characteristics of F1 varieties in crops.
What are hybrid plants?
Hybrid plants are plants that result from crossing two different varieties, usually with the aim of obtaining new characteristics or qualities. This process of hybridization is commonly used in agriculture and horticulture to improve productivity, disease resistance, flavor, color or other aspects of plants.
Hybrid plants can be created by crossing plants belonging to the same species but different varieties, or by crossing plants belonging to different species. Cross-breeding can be carried out naturally, by cross-pollination, or artificially, where plants are pollinated by hand.
It's important to note that hybrid plants are not genetically modified organisms (GMOs). GMOs are plants whose genetic material has been modified by genetic engineering techniques, whereas hybrid plants are created by natural or artificial crossing without direct genetic manipulation.
Hybrid plants have enjoyed great success in modern agriculture due to their agronomic advantages and their ability to meet growing food production demands. However, some critics point out that hybrid plants can be less adapted to certain environments and often require the purchase of new seeds each year, which can lead to economic dependence for farmers.
In a nutshell, hybrid plants are plants obtained by crossing two different varieties with the aim of improving their characteristics. This technique is commonly used in agriculture to increase plant productivity and resistance, but it can also have its drawbacks.
How can you tell if a plant is a hybrid?
To know if a plant is a hybrid, there are a few distinctive signs to observe:
1. Visual appearance : Hybrid plants may have physical characteristics that differ from traditional varieties. They may have bright colors, unusual shapes or unique patterns.
2. Labeling : If you buy a plant in a specialist store, it may be labelled as a hybrid. Growers often inform consumers of the hybrid nature of a plant to facilitate identification.
3. Reproduction : When you try to reproduce a hybrid plant, you may find that its seeds do not give the same characteristics as the parent plant. Hybrid plants are generally sterile, or their offspring show significant variations from the original plant.
4. Producer information : If you obtain a plant from a professional grower, he or she can provide you with specific information on the hybrid variety and its distinctive characteristics.
However, it's important to note that some hybrids can look very similar to traditional varieties, and it can be difficult to tell them apart without the appropriate information. When in doubt, it's always best to seek the advice of a gardening expert or refer to reliable sources for accurate information on a given plant.
In conclusion, hybrid plants have both advantages and disadvantages. On the one hand, they offer increased productivity, better resistance to disease and difficult environmental conditions. What's more, their appearance is often aesthetically appealing. These characteristics make hybrid plants a popular choice for growers and gardeners alike.
On the other hand, hybrid plants can be more expensive to grow, due to the need to buy them every year rather than harvesting seeds from the mother plants. What's more, their reproduction is often sterile, limiting the possibility of growing them yourself.
However, it is important to note that hybrid plants have played a crucial role in increasing food production worldwide, helping to feed a growing population. They have also improved crop quality and diversity.
Ultimately, the choice between hybrid and traditional plants depends on each individual's needs and objectives. Hybrid plants offer positive qualities, but can also present constraints. It's essential to weigh up the pros and cons before making an informed choice for our garden or farm.