The advantages and disadvantages of using GMOs are a controversial subject that divides opinions. On the one hand, they offer the potential to increase agricultural yields and resist disease. On the other, their use raises concerns about human health and environmental impact. This article examines the arguments for and against their use, with the aim of providing a balanced perspective on this complex issue.
C'est pas sorcier -AGRI.BIO
[arve url="https://www.youtube.com/embed/QioWHYGCX70″/]
What are the advantages of GMOs?
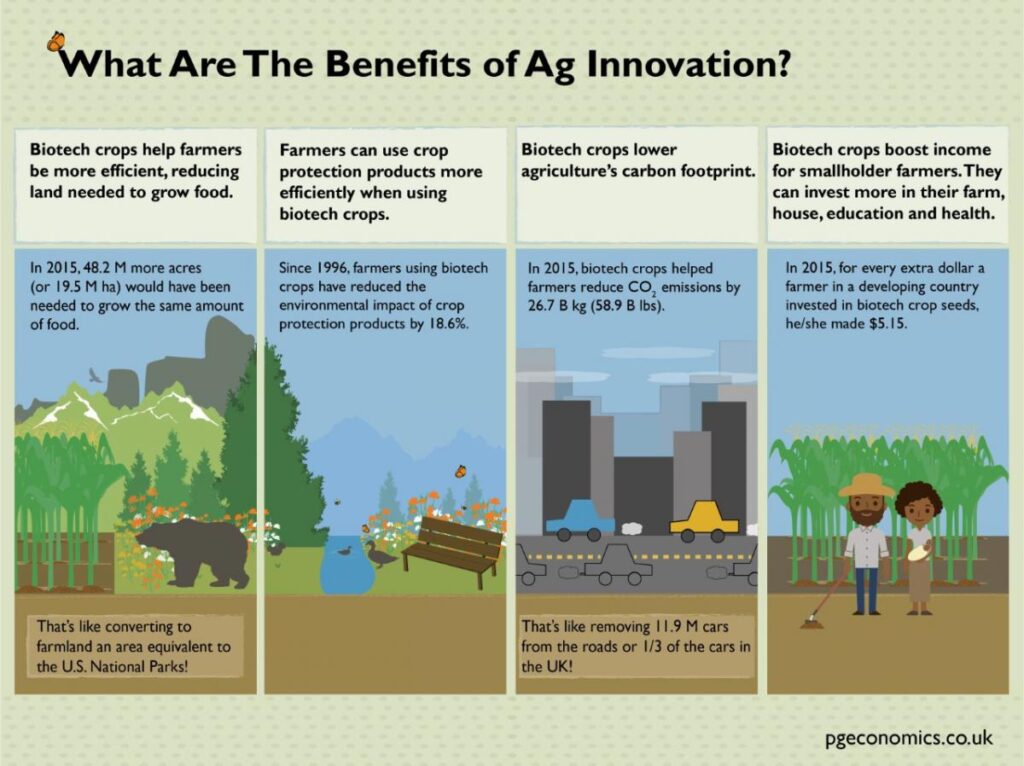
The benefits of genetically modified plants (GMPs) are many and varied.
First of all, GMPs make it possible to increase crop yields, which is particularly important in the current context of population growth. By genetically modifying plants, it is possible to make them more resistant to disease, pests and adverse climatic conditions, resulting in higher productivity. This helps to ensure global food security by increasing the availability of foodstuffs.
What's more, GMPs can reduce the use of chemical pesticides and herbicides. By introducing genes that give plants natural resistance to pests or weeds, it is possible to limit the use of chemicals that are harmful to the environment and human health. This promotes more sustainable, environmentally-friendly agriculture.
GMPs can also help improve the nutritional quality of crops. For example, plants can be enriched with essential vitamins or minerals, which can help prevent dietary deficiencies in populations most affected by them.
Finally, GMPs offer new opportunities for the development of drugs and industrial products. Some genetically modified organisms can be used as "biological factories" to produce valuable medical substances or industrial materials.
However, it is important to take into account the possible risks associated with the use of GMPs, such as the uncontrolled dissemination of modified genes in the environment or the appearance of resistance in pests. In-depth studies and strict regulations are therefore needed to guarantee the safety and harmlessness of GMPs.
In short, although GMPs are not without controversy, their potential benefits in terms of food security, environmental sustainability, nutrition and economic development are considerable.
What are the disadvantages of GMOs?
The use of GMOs (Genetically Modified Organisms) has several disadvantages. Here are some of the main ones:
1. Health risk : Some scientists and environmental groups argue that GMOs could have negative effects on human health. Some studies suggest that consumption of genetically modified foods could be linked to health problems such as allergies, digestive disorders or even certain types of cancer. However, it should be noted that scientific opinion is divided on this subject.
2. Environmental impact : GM crops can have a negative impact on the environment. For example, genetically modified plants resistant to herbicides can lead to increased use of these chemicals, which can pollute soil and groundwater. What's more, the release of modified genes into the wild can have unpredictable consequences for local ecosystems and biodiversity.
3. Monopoly of large companies: GMO production is often associated with large agribusinesses. These companies hold patents on genetically modified seeds, which can lead to market monopolization. This limits crop diversity and choice for farmers, who may be forced to buy patented seeds at high prices.
4. Lack of transparency: The GMO debate is often marred by a lack of transparency. GMO advocates claim that these technologies are safe and effective, but critics argue that there is a lack of independent research and that GMO safety studies are often funded by the industry itself. This raises questions about the reliability of the data available on GMOs.
It is important to note that some people also support the potential benefits of GMOs, such as the possibility of producing more food for a growing population or solving food safety problems. However, the disadvantages mentioned above should be taken into account when considering the use of GMOs in the context of current events.
What are the environmental benefits of GMOs?
GMOs (genetically modified organisms) have certain potential benefits for the environment. Here are some of the most commonly cited benefits:
1. Disease and pest resistance : Genetically modified plants can be engineered to resist disease and pests, reducing the need for chemical pesticides. This can help protect biodiversity by reducing the negative impact of pesticides on ecosystems.
2. Water and resource conservation : Some GMOs are designed to be more resistant to drought and other harsh environmental conditions. This makes it possible to grow crops in areas where water is scarce, helping to conserve water resources.
3. Increased yield : GMOs can be modified to produce higher yields, which can help meet the world's growing demand for food. By increasing agricultural productivity, pressure on farmland can be reduced and deforestation prevented.
4. Reduce the use of chemical inputs : Some GMOs are designed to resist herbicides, thus reducing the use of these potentially environmentally damaging chemicals. This can help preserve soil and water quality.
However, it is important to stress that GMOs also raise health and environmental concerns. It is essential to carry out thorough, independent studies to assess potential risks before GMOs are widely used.
In conclusion, the use of GMOs presents both benefits and disadvantages. On the one hand, GMOs make it possible to increase crop yields, solve malnutrition problems, and develop disease- and pest-resistant varieties. They can also reduce the use of agricultural chemicals, thereby helping to protect the environment.
On the other hand, there are concerns about the risks to human health and the environment. Some fear that consuming GMOs could have harmful effects on our health in the long term. In addition, there are concerns about the impact of GMOs on biodiversity, as they could threaten native species. In addition, it is important to consider the interests of local farmers, who could be affected by competition from GM products.
It is therefore essential to continue in-depth research into GMOs in order to better understand their potential effects. Appropriate regulation and labelling are also needed to inform and give choice to consumers. Ultimately, the decision on whether or not to use GMOs must be based on a balanced assessment of the advantages and disadvantages, while taking account of the precautionary principle.