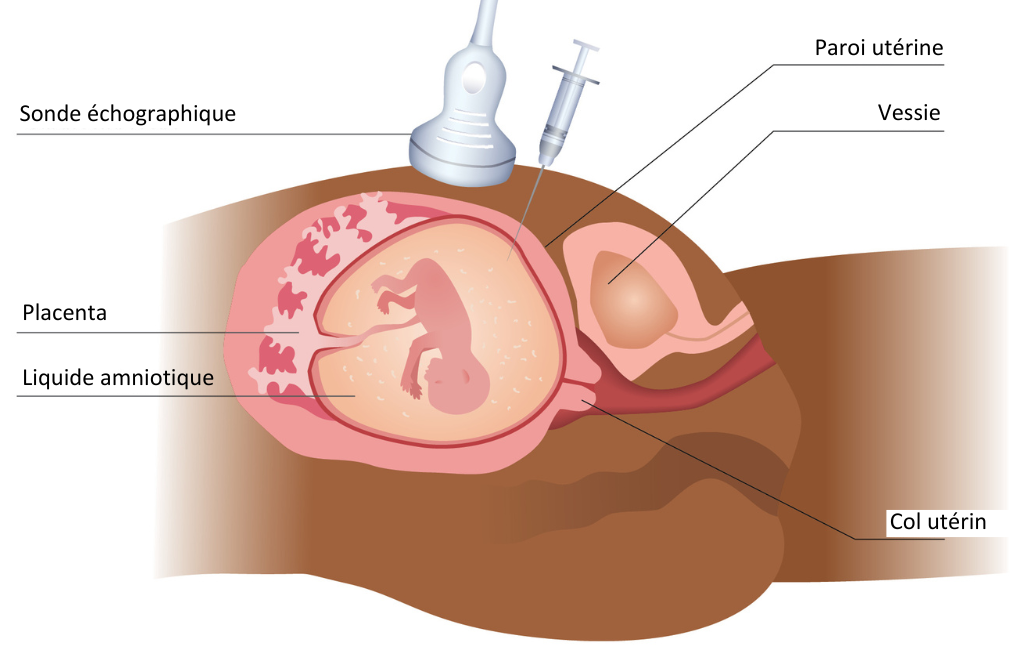
Amniocentesis is a prenatal test commonly used to detect chromosomal abnormalities in the fetus. The procedure involves taking a sample of the amniotic fluid surrounding the baby in the uterus. Although it provides valuable information on the health of the fetus, it is not a complete test, amniocentesis has both advantages and disadvantages. So it's important to weigh up the pros and cons before making a decision about this test.
[AVS] Accelerate your metabolism to reverse aging! - Dr Christophe de Jaeger
[arve url="https://www.youtube.com/embed/GO9A6FtXW5s "/]
What are the risks of amniocentesis?
Amniocentesis is a medical procedure used to diagnose certain genetic abnormalities in the fetus during pregnancy. While it can provide valuable information, there are also risks associated with this procedure.
1. Risk of miscarriage: Amniocentesis carries a risk of miscarriage, estimated at between 0.5% and 1%. This means that there is a small possibility that the procedure will result in the loss of the fetus.
2. Infection: Although rare, there is a risk of infection after amniocentesis. This can lead to complications for both mother and fetus.
3. Bleeding: Amniocentesis may cause slight bleeding in the uterus. In most cases, this bleeding is minimal and resolves quickly. However, it is important to monitor any abnormal bleeding.
4. Other complications: Although very rare, other complications can arise during amniocentesis, such as perforation of the uterine wall or an allergic reaction to the drugs used during the procedure.
It is essential to discuss these risks with your healthcare professional before deciding to undergo amniocentesis. He or she can assess your medical history and specific risk factors to give you a more accurate estimate of potential risks.
Who should have amniocentesis?
Who should have amniocentesis?
Amniocentesis is a prenatal test in which a sample of amniotic fluid is taken from around the fetus. This test is generally offered to pregnant women at high risk of complications or congenital malformations in their fetus.
The main indications for amniocentesis are as follows:
1. Advanced maternal age : Pregnant women aged 35 and over are at increased risk of developing trisomy 21 (Down's syndrome) in their fetus. Amniocentesis may be recommended to confirm the diagnosis.
2. Family history : If there is a family history of genetic or chromosomal disease, amniocentesis may be proposed to assess the risk of transmission to the unborn child.
3. Abnormal results of prenatal screening tests : If the results of a prenatal screening test (such as nuchal translucency measurement or serum markers) are abnormal, amniocentesis may be recommended to confirm or exclude certain chromosomal abnormalities.
4. Previous pregnancies with chromosomal or genetic abnormalities : If a woman has already had a pregnancy with a chromosomal or genetic abnormality, amniocentesis may be proposed to assess the risk of recurrence.
It is important to note that amniocentesis is not mandatory, and that each case must be evaluated individually according to specific risk factors. A thorough medical consultation is necessary to determine whether amniocentesis is recommended in a given context.
It is advisable to consult a healthcare professional for accurate, up-to-date information on the indications and implications of amniocentesis.
Is amniocentesis mandatory?
No, amniocentesis is not mandatory.
Amniocentesis is a medical procedure involving the removal of a small quantity of amniotic fluid from around the fetus. This procedure is generally offered to pregnant women with a high risk of certain genetic diseases in the fetus, such as trisomy 21. However, there is no guarantee that this will be the case, the decision to undergo amniocentesis belongs to the pregnant woman and is not imposed. Doctors provide detailed information on the benefits, risks and limitations of this procedure, so that the woman can make an informed decision. It is important to consult a healthcare professional to discuss the options available and determine whether amniocentesis is necessary in a particular case.
Does amniocentesis hurt?
Amniocentesis is a medical procedure used to take a sample of the amniotic fluid surrounding the fetus during pregnancy. During this procedure, a fine needle is inserted through the mother's abdomen and into the uterus. Although each person may feel the pain differently, in general, most women describe the sensation as being similar to that of a sting or pinch.
However, it is important to note that amniocentesis is generally performed under the supervision of a physician. local anaestheticThis means that the area where the needle is inserted is numbed. This can help reduce the discomfort and pain associated with the procedure. In addition, your doctor will give you instructions before the amniocentesis to help you relax and give you advice on pain management.
It is always advisable to discuss your concerns and expectations with your doctor before undergoing any medical procedure. Your doctor will be able to provide you with comprehensive information about the procedure, including potential risks and pain management strategies.
In conclusion, it's important to weigh up the pros and cons of amniocentesis carefully before deciding on the procedure. On the one hand, amniocentesis provides valuable information about the health of the fetus, and can help detect certain genetic anomalies. This enables parents to make informed decisions about their pregnancy and prepare for any medical challenges that may arise.
However, it is also important to consider the risks associated with this invasive procedure. Amniocentesis carries a slight risk of miscarriage, premature rupture of membranes and infection. What's more, the process can be stressful for parents, as it involves waiting for results and the possibility of having to make difficult choices.
It is therefore advisable to consult a healthcare professional and discuss the advantages and disadvantages specific to each individual case. The decision to undergo amniocentesis must be based on the needs and priorities of each family, taking into account both medical and emotional aspects. Ultimately, this personal choice must be made with full knowledge of the facts, relying on medical advice and considering the advantages and disadvantages of this delicate procedure.