Transgenesis, a controversial technique which involves introducing foreign genes into a living organism, has both considerable advantages and potential drawbacks. On the one hand, it enables the creation of disease- and herbicide-resistant plants, which can significantly increase agricultural yields. However, this genetic manipulation raises ethical and environmental concerns, as well as questions about food safety. A thorough analysis of the benefits and risks is needed to assess the real impact of transgenesis on our societies.
Open Winter Party GIFTS on Fortnite!!
[arve url="https://www.youtube.com/embed/tR1WXBC7ozI "/]
What are the advantages of transgenesis?
Transgenesis offers a number of advantages in various fields. In particular, it can be used to modify the genetic characteristics of living organisms. by adding specific genes from other species. Here are some of the major advantages of transgenesis:
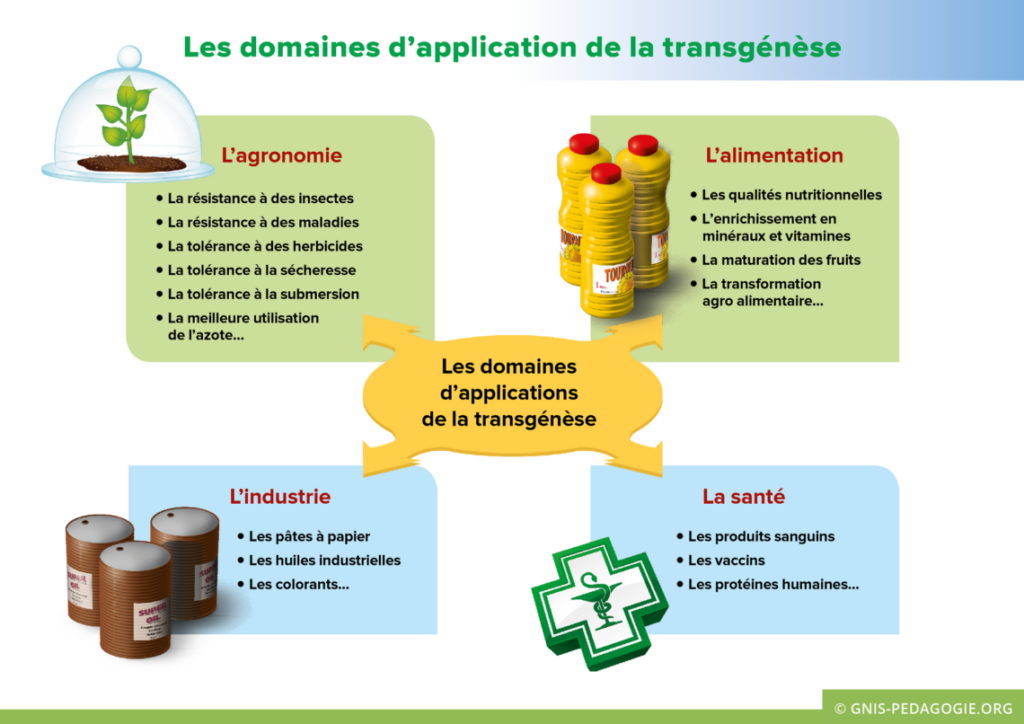
1. Improving agricultural yields : Transgenesis makes it possible to create plants that are resistant to disease, pests or adverse climatic conditions. This can help increase crop yields, reduce pesticide use and prevent crop losses.
2. Improving food quality: Transgenesis can be used to improve the nutritional quality of foods by enriching their composition with vitamins, minerals or antioxidants. It can also help reduce the content of allergens or undesirable substances in foods.
3. Disease prevention : Transgenesis offers promising possibilities in the field of medicine. It can be used to produce more effective drugs, such as vaccines or therapeutic proteins, in living organisms.
4. Environmental conservation : Thanks to transgenesis, it is possible to develop plants that require less water, fertilizer or chemical products, thus contributing to the preservation of the environment and the sustainability of agriculture.
5. Scientific advances : Transgenesis enables researchers to study how genes work, and to gain a better understanding of complex biological mechanisms. It therefore fosters scientific advances in many fields, such as genetics, molecular biology and medicine.
It's important to note that transgenesis also raises ethical, environmental and safety issues that need to be taken into account.
What are the disadvantages of transgenesis?
Transgenesis, which involves inserting foreign genes into the genome of an organism, has a number of disadvantages to consider. First and foremost, environmental impact are a cause for concern. Transgenic plants can crossbreed with wild species and introduce undesirable traits into the ecosystem. What's more, some transgenic crops require the use of pesticides, which can have a detrimental impact on biodiversity and health.
Effects on human health are also a cause for concern. Although genetically modified organisms (GMOs) are generally considered safe for human consumption, some studies suggest potential adverse effects, including allergies and hormone disruption.
In addition, economic and social aspects of transgenesis is often criticized. Large agribusinesses that control GM technology can exercise a monopoly on seeds, limiting crop diversity and making farmers more dependent. In addition, there are debates about intellectual property and farmers' rights to reuse their own seeds.
It's important to stress that these drawbacks don't necessarily mean that transgenesis is totally harmful. Some genetic modifications can bring significant benefits, such as disease and pest resistance, as well as improved crop yields. However, it is crucial to weigh up the potential benefits against the risks and drawbacks in order to make informed decisions.
What are the disadvantages of genetic engineering?
The disadvantages of genetic engineering are numerous and must be taken into account when evaluating this technology. Here are just a few of them:
1. Risks to human health : There are concerns about the potential effects on human health associated with the consumption of genetically modified (GM) products. Some scientists are concerned that genetic modifications could have unforeseen and undesirable effects on the human organism.
2. Environmental impact : Genetically modified crops can have an impact on the environment. GM plants can cross-breed with wild species, leading to the spread of modified genes in the wild. This could have harmful consequences for the genetic diversity of plant and animal populations, as well as for surrounding ecosystems.
3. Farmers' dependence : GM crops are often patented by agrochemical companies, which means that farmers have to buy seeds every year rather than reusing them. This can make farmers dependent on large corporations and affect their ability to make independent decisions about their farming practices.
4. Superpredator resistance : Some genetically modified organisms are designed to resist insect pests or herbicides. However, this may lead to the emergence of resistant superpredators, requiring ever-increasing quantities of herbicides or the use of new chemicals to control them.
5. Ethics and social impact : Genetic engineering also raises ethical questions, particularly with regard to the manipulation of human genes and the modification of nature itself. Moreover, some fear that this technology will further widen inequalities in terms of access to suitable agricultural resources, reinforcing the differences between developed and developing countries.
It is crucial to take these drawbacks into account when assessing the adoption and use of genetic engineering, to ensure responsible use of this technology.
What are the advantages of OMG?
GMOs, or genetically modified organisms, offer a number of potential advantages for agriculture and food safety:
1. Increased efficiency : OMGs can be genetically modified to resist disease, pests and harsh weather conditions, resulting in higher yields for farmers.
2. Reducing the use of pesticides : Some GMOs have been designed to be resistant to pests, thus reducing the use of chemical pesticides that are harmful to the environment and human health.
3. Increased nutritional value : GMOs can be modified to be richer in essential nutrients such as vitamins and minerals, helping to improve the nutritional value of crops.
4. Better food preservation : Some GMOs are designed to have a longer shelf-life, which can reduce food losses and contribute to global food security.
5. Adapting to environmental constraints : GMOs can be created to resist specific environmental conditions, such as drought or nutrient-poor soils. This can enable farmers to grow crops in areas previously unsuitable for agriculture.
However, it should be noted that opinions on GMOs are divided, and there are concerns about their impact on the environment, human health and biodiversity. In-depth studies and appropriate regulation are needed to ensure their safe and responsible use.
In conclusion, transgenesis has both advantages and disadvantages. On the one hand, it makes it possible to develop plant varieties resistant to disease, pests and harsh environmental conditions, which can help to ensure growing global food security. In addition, it offers the possibility of producing medicines and vaccines more efficiently, thanks to the production of recombinant proteins in plants.
HoweverTransgenesis also raises concerns in terms of risks to human health and the environment. The long-term effects of transgenic crops on health are not yet fully understood, and there are concerns about the spread of modified genes into natural populations, which could lead to a loss of biodiversity.
It is therefore essential to carry out more research in order to thoroughly assess the consequences of transgenesis, in terms of both health and the environment. Strict, transparent regulations must also be put in place to govern the use of genetically modified organisms (GMOs) and ensure responsible use of this technology.
In short, transgenesis offers interesting possibilities for improving agriculture and health, but requires a rigorous assessment of potential benefits and risks. The aim must be to strike a balance between scientific innovation and the protection of the environment and public health.