Genetic transformation, also known as genetic modification, is a controversial subject with both advantages and disadvantages. While this technology offers the possibility of developing crops that are more resistant to disease, pests and harsh environmental conditions, it also raises ethical and environmental concerns. This article takes a close look at the different aspects of this practice, and helps to better understand the issues involved in genetic modification of plants and animals.
The method to get 20/20 at the last moment 🔥⚔
[arve url="https://www.youtube.com/embed/CRh6XORk3gg "/]
What are the advantages of OMG?
Genetically modified organisms (GMOs) offer a number of advantages in the agricultural and food sectors. Here are some of the main ones:
1. Increased efficiency : Genetically modified plants can be engineered to resist disease, adverse climatic conditions and pests, significantly improving their yield. This makes it possible to produce more food to meet the growing demand of the world's population.
2. Herbicide resistance : Some GMOs are designed to resist herbicides, enabling farmers to control weeds more effectively without harming crops. This reduces the use of environmentally harmful herbicides and promotes better management of natural resources.
3. Improved food quality : GMOs can be modified to contain essential nutrients, such as vitamins and minerals, offering better nutritional quality in the diet. For example, some genetically modified rice varieties contain more vitamin A, which can help prevent blindness in populations deficient in this vitamin.
4. Environmental sustainability : GMOs can help reduce the use of chemical pesticides, which in turn reduces the negative impact on the environment and human health. In addition, some GMOs can reduce soil erosion and water consumption, promoting more sustainable agriculture.
Nevertheless, it should be stressed that the debates surrounding GMOs remain controversial, particularly with regard to their effects on human health and the environment. It is therefore essential to pursue research and rigorously regulate their use in order to maximize benefits while minimizing potential risks.
What are the disadvantages of GMOs?
Genetically modified organisms (GMOs) are often controversial because of their potentially negative impact on the environment and human health. Here are some of the disadvantages associated with GMOs:
1. Environmental impact : GM crops can lead to a reduction in biodiversity, as some genetically modified plants can become invasive and crowd out native species. What's more, GMOs can also contaminate traditional varieties through cross-pollination, which can be detrimental to farmers wishing to save unmodified seeds.
2. Health effects : Although studies on the effects of GMOs on human health are still ongoing, there are concerns about their potential impact on allergies, antibiotic resistance and other adverse reactions. As a result, some groups argue that the widespread use of GMOs in our food supply could present health risks.
3. Dependence on large companies : GM crops are generally owned by large agrochemical companies, which can lead to farmers becoming economically dependent on these companies. Some fear that this limits farmers' choice and contributes to a concentration of power in the agricultural sector.
4. Lack of transparency : There is criticism of the lack of regulation and transparency surrounding GMOs. Some feel that consumers are not sufficiently informed about the presence of GMOs in their food, which limits their ability to make informed choices.
It is important to note that some of these concerns are still being debated, and that scientific research into GMOs is constantly evolving. However, it is essential to inform the public about the various aspects of GMOs in order to encourage constructive debate and informed decision-making.
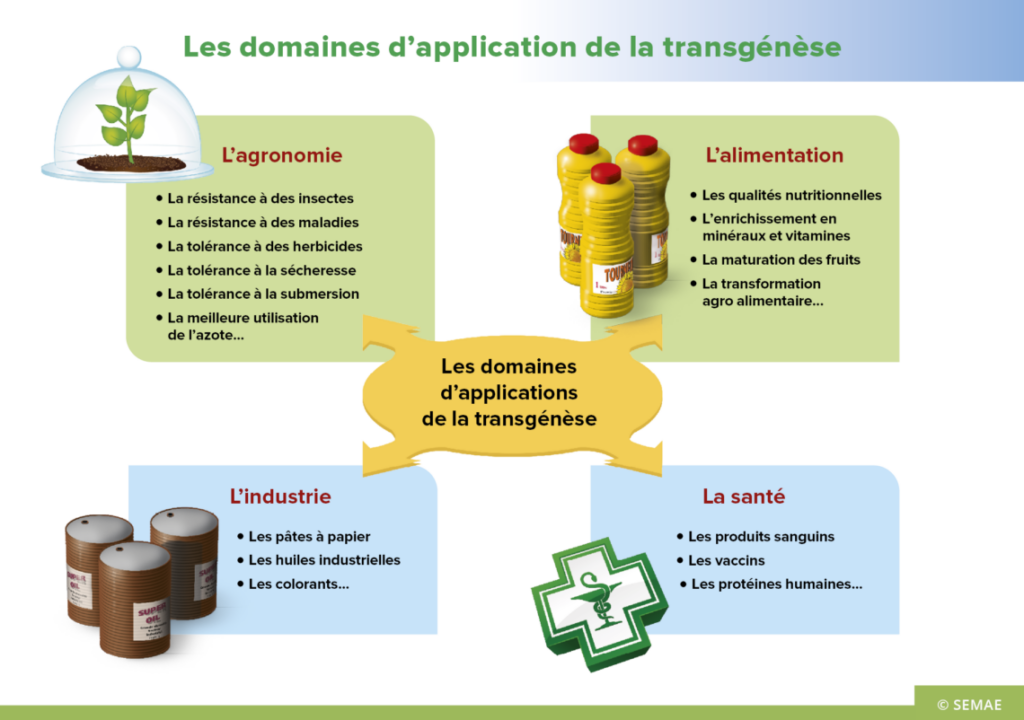
What are the advantages of transgenesis?
Transgenesis offers several advantages in the field of scientific research and innovation.
Firstly, it allows you to genetically modify living organismsThe aim is to introduce specific characteristics into plants, animals or even micro-organisms. These may include disease resistance, improved nutritional quality or increased agricultural yields. These genetic modifications can help solve major environmental and food problems.
In the medical fieldTransgenesis has led to significant advances in the development of innovative drugs and therapies. For example, it is used to produce therapeutic proteins such as insulin or monoclonal antibodies. It also offers promising prospects in the field of regenerative medicine, notably for the production of artificial tissues and organs.
Transgenesis is also a valuable tool for basic research. By modifying an organism's genes, scientists can better understand how genes and biological processes work. The result is a deeper understanding of the biology, physiology and genetics of living organisms.
However, it is important to note that transgenesis also raises ethical and environmental questions. Some are concerned about the potential risks to human health and the environment, as well as the possible consequences for biodiversity. It is therefore essential to strictly regulate the use of transgenesis in order to minimize these risks.
In conclusion, transgenesis offers many advantages in different scientific fields, including agricultural, medical and basic research. However, potential benefits need to be carefully weighed against risks and ethical concerns when applying it.
What are the advantages of genetic manipulation?
Genetic manipulation offers several potential advantages. Firstly, it offers the possibility of correct hereditary genetic diseasesby modifying the genes responsible for these diseases. This could save lives and improve quality of life for many people.
Genetic manipulation can also be used to improve physical and mental characteristics of individuals. For example, it could enable the development of treatments to prevent or reverse aging, improve memory, or increase physical capacity.
In addition, genetic manipulation offers the possibility of modify plants and animals to improve their productivity and resistance to disease and harsh environmental conditions. This could help combat world hunger and protect biodiversity.
However, it is important to underline the ethical concerns and potential risks associated with genetic manipulation.. Strict regulations and responsible use of this technology are essential to avoid abuse and unintended consequences for health and the environment.
In conclusion, genetic transformation has both advantages and disadvantages. On one side, it offers numerous opportunities for crop and species improvement, helping to boost agricultural yields and solve the world's famine problems. It can also contribute to the production of more effective medicines and to scientific research.
However, on the other hand, Genetic manipulation raises ethical and environmental concerns. The long-term effects on biodiversity and human health are not yet clearly established, and there are potential risks to the environment when modified genes are released. In addition, it is important to ensure adequate regulation to avoid abuse and adverse consequences.
It is therefore crucial to strike a balance between the potential benefits of genetic transformation and ethical and environmental concerns. It is essential to conduct in-depth research and promote open, transparent dialogue between scientists, policy-makers and the general public in order to make informed, responsible decisions. This will maximize the benefits of this technology while minimizing potential risks.