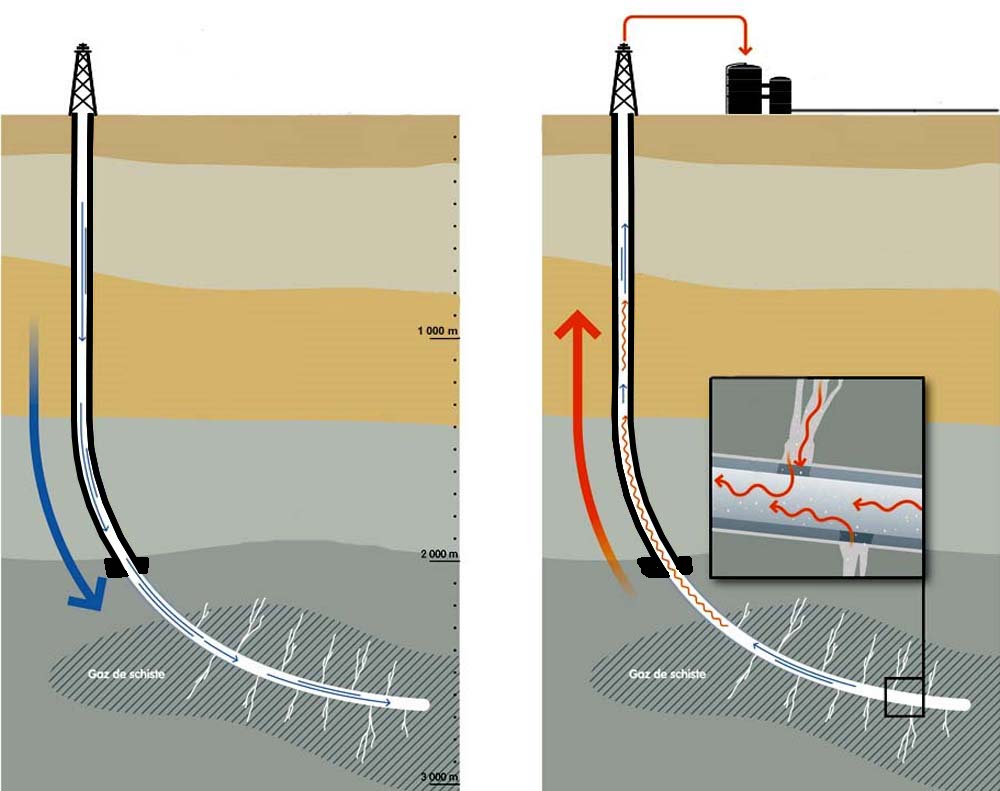
Shale gas is a controversial energy resource whose exploitation is the subject of heated debate. This form of natural gas is trapped in deep sedimentary rock known as shale. Its complex geology makes it more difficult to exploit than conventional gas. However, some voices point to the economic benefits and reduced greenhouse gas emissions it can offer. Nevertheless, shale gas extraction also has considerable environmental and social drawbacks.
UKRAINE, RUSSIA, NATO: GENERAL VINCENT DESPORTES DENOUNCES OUR WAR STRATEGY
[arve url="https://www.youtube.com/embed/eNgtlTWcmDw "/]
Why use shale gas?
Shale gas is often used because of its many advantages.
First and foremost, it offers countries greater energy independence. By exploiting their domestic shale gas resources, countries reduce their dependence on natural gas imports, thereby boosting their energy security and self-sufficiency.
What's more, shale gas is a cheap and abundant source of energy. Its exploitation enables us to meet the growing demand for energy while offering relatively low production costs. This abundance of energy can also help stabilize market prices and reduce energy price fluctuations.
In addition, using shale gas can help reduce greenhouse gas emissionscompared with other fossil fuels such as coal. Shale gas produces less carbon dioxide when burned, making it a cleaner alternative for power generation.
However, it's worth mentioning that the use of shale gas is not without controversy. Some people are concerned about the environmental consequences of its extraction, particularly with regard to the potential risks of groundwater contamination and induced earthquakes. Strict regulations and responsible extraction practices are therefore essential to minimize these negative impacts.
In conclusion, the use of shale gas offers advantages in terms of energy independence, availability and reduction of greenhouse gas emissions. However, it is important to take environmental concerns into account and promote responsible use of this resource.
Is shale gas a pollutant?
Yes, shale gas is considered a pollutant. Extracting shale gas involves a technique called hydraulic fracturing, which uses huge quantities of water, mixed with chemicals, to release the gas trapped in underground rocks.
This technique presents several major environmental problems:
1. Water contamination : There is a risk of contamination of groundwater by the chemicals used in hydraulic fracturing. These chemicals can be hazardous to human and animal health.
2. Excessive water use : Hydraulic fracturing requires huge quantities of water, which can exacerbate water shortage problems in certain regions already affected by drought.
3. Greenhouse gas emissions : Extracting, processing and transporting shale gas generates significant greenhouse gas emissions, contributing to climate change.
4. Seismic risk : Hydraulic fracturing activity can cause earthquakes, albeit often of low magnitude.
Because of these environmental impacts, shale gas is generally considered a polluting non-renewable energy source.
What are the consequences of exploiting shale oil?
The exploitation of shale oil has major consequences for the environment and society. From an environmental standpointHowever, this method of extraction requires the use of large quantities of water and chemicals, which can lead to a significant loss of energy. water pollution and groundwater. What's more, shale oil wells are often associated with leaks of methane, a greenhouse gas that is potentially dangerous for the climate.
At company levelShale oil development can lead to conflicts over land use and access to natural resources. It can also have adverse effects on local communities, particularly in terms of air quality, noise pollution and health problems linked to the proximity of extraction sites.
It's also worth mentioning that exploiting shale oil can have economic consequences, as it can lead to increased dependence on fossil fuels and hinder the development of renewable energies.
In conclusion, while the exploitation of shale oil may offer an additional source of energy in the short term, it is important to consider the environmental, social and economic consequences associated with this practice.
Why isn't shale gas being exploited in France?
Shale gas is not being exploited in France for a number of reasons.
Firstly, there is strong opposition from local populations and environmental associations. The latter point to the potential risks associated with shale gas development, such as groundwater contamination, land fragmentation and air pollution. This opposition led to the adoption in 2011 of a law banning hydraulic fracturing, the technique used to extract shale gas.
What's more, France is committed to the energy transition and has set ambitious targets for renewable energies. Exploitation of shale gas would therefore contradict these objectives and could compromise efforts to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and combat climate change.
Finally, France is also subject to geological constraints. Shale gas reserves are smaller than in other countries, such as the United States. What's more, French deposits are often located in densely populated areas, making it difficult to exploit them in compliance with safety and environmental protection standards.
In conclusion, France is not exploiting shale gas due to opposition from civil society, renewable energy commitments and geological constraints.
In conclusion, shale gas is an energy resource with both advantages and disadvantages. From a geological point of view, it is important to emphasize that this form of gas is found in deep sedimentary rock, which requires specific exploitation techniques, such as hydraulic fracturing.
On the one hand, exploiting shale gas can help diversify energy sources and reduce dependence on traditional fossil fuels. It can also create jobs and stimulate the local economy. However, it is crucial to consider the environmental and health consequences associated with such exploitation.
On the environmental frontThe hydraulic fracturing required to extract shale gas can entail risks of groundwater contamination and greenhouse gas emissions. In addition, the intensive use of water may have an impact on already limited freshwater reserves.
On the health frontthe use of chemicals in the hydraulic fracturing process raises concerns about their impact on human health. Studies are still needed to fully assess the potential risks.
It is therefore essential to introduce strict regulations and rigorous controls to minimize negative impacts on the environment and public health. Research and development of cleaner, more sustainable energy technologies must also be further promoted.
In short, the exploitation of shale gas presents economic opportunities, but requires a cautious and responsible approach to ensure the protection of our environment and our health. This is a major challenge facing decision-makers, scientists and society as a whole.